Creating a Multi-Select Drop-Down List in Excel: Two Techniques
Creating an Excel drop down list with multiple selections can significantly enhance your spreadsheets’ functionality and user experience. Whether you’re utilizing Excel for personal or professional tasks, this feature can be handy for various purposes such as tagging, categorization, data filtering, and more. By implementing this technique, you can streamline data entry processes, improve data organization, and boost overall productivity in your Excel usage.
When working with large sets of data, having the option to select multiple items from a drop-down list can significantly expedite the task of categorizing or tagging entries. This is especially advantageous in scenarios where a single entry may belong to multiple categories or require multiple tags. By allowing for multiple selections in a drop-down list, you can efficiently capture these nuances without the need for complex workarounds or manual entry duplication.
Furthermore, the ability to create a drop-down list with multiple selection support in Excel provides a versatile solution for various use cases across different industries and roles. For instance, in project management, this feature can be utilized to assign tasks to multiple team members, select relevant project phases, or indicate the priority level of tasks. In an educational setting, it can facilitate the grading process by enabling educators to select multiple categories or criteria for assessment. The applications extend to fields such as sales, inventory management, and more, where the need for flexible data input and analysis is paramount.
By exploring and implementing the methods for creating a multi-select drop-down list in Excel, you open up new possibilities for managing and leveraging data within your spreadsheets. Whether for personal projects, academic pursuits, or professional endeavors, this functionality can serve as a valuable asset, empowering you to efficiently handle and interpret data with enhanced precision and agility.
Excel Drop Down List Multiple Selection – Video Tutorial
Technique 1: Single Drop-Down List on a Specific Sheet
This method targets a single drop-down list on a specific sheet, allowing users to select multiple items from the list.
Steps:
- Create Your List: Enter your list of items in a column, e.g., Column A.
- Name the Range: Define the range for the list items.
- Create the Drop-Down List: Use data validation to create a drop-down list.
- Enable Multiple Selections with VBA:
- Open the VBA editor (Alt + F11).
- Insert the following code in the specific sheet’s code window:
'--------------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Enable multi-select drop-down on THIS specific sheet
' while allowing partial edits (removing individual items) and
' the ability to clear the cell completely.
'
' How it works:
' 1) For any single-cell change, check if the cell has list-based data validation.
' 2) If the user selected exactly one new item from the drop-down,
' we append it to existing items, unless it’s already there (to avoid duplicates).
' 3) If the user cleared or manually edited the cell, we allow that change to stand.
'--------------------------------------------------------------------
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
On Error GoTo CleanExit
' Ensure only one cell is changed at a time
If Target.Count > 1 Then GoTo CleanExit
' Check if cell has data validation of type List
If Not HasDataValidation(Target) Then GoTo CleanExit
' Temporarily disable events to avoid looping
Application.EnableEvents = False
Dim newValue As String
Dim oldValue As String
' Capture what the user entered/selected
newValue = Target.Value
' Undo the change to get the old value
Application.Undo
oldValue = Target.Value
' Restore the new value to the cell
Target.Value = newValue
' If the user cleared the cell, allow it to remain blank
If newValue = "" Then
' Nothing extra needed; the cell is now blank.
Else
' Fetch the valid items from the data validation source
Dim validationItems As Variant
validationItems = GetValidationList(Target)
Dim userPickedFromList As Boolean
userPickedFromList = False
' Check if newValue exactly matches ONE item in the drop-down
If Not IsEmpty(validationItems) Then
Dim i As Long
For i = LBound(validationItems) To UBound(validationItems)
If Trim(newValue) = Trim(validationItems(i)) Then
userPickedFromList = True
Exit For
End If
Next i
End If
' If user selected a valid drop-down item and the old cell wasn't empty
If userPickedFromList And (oldValue <> "") Then
' Split the old cell contents by commas
Dim oldArray As Variant
oldArray = Split(oldValue, ",")
Dim alreadyExists As Boolean
alreadyExists = False
' Check if newValue already exists in oldValue
For i = LBound(oldArray) To UBound(oldArray)
If Trim(oldArray(i)) = Trim(newValue) Then
alreadyExists = True
Exit For
End If
Next i
If Not alreadyExists Then
' Append new item with a comma
Target.Value = oldValue & ", " & newValue
Else
' Do not duplicate it
Target.Value = oldValue
End If
' If user selected a valid drop-down item and old cell was empty
ElseIf userPickedFromList And (oldValue = "") Then
' Just put the new item in the cell
Target.Value = newValue
Else
' The user typed/edited manually rather than picking a single list item
' -> We respect the manual edit and leave newValue as is.
' (No extra code needed, since Target.Value = newValue already.)
End If
End If
CleanExit:
' Re-enable events
Application.EnableEvents = True
End Sub
'--------------------------------------------------------------------
' Checks if the cell has data validation of type List (3).
'--------------------------------------------------------------------
Function HasDataValidation(cell As Range) As Boolean
Dim validationType As Long
On Error Resume Next
validationType = cell.Validation.Type
On Error GoTo 0
HasDataValidation = (validationType = 3)
End Function
'--------------------------------------------------------------------
' Returns the drop-down list items as a 1D array (if any).
' Handles both direct typed lists (comma-separated) and range references.
'--------------------------------------------------------------------
Function GetValidationList(cell As Range) As Variant
Dim formulaStr As String
On Error Resume Next
formulaStr = cell.Validation.Formula1
On Error GoTo 0
If Left(formulaStr, 1) = "=" Then
' It's referencing a range or named range
Dim rng As Range
On Error Resume Next
Set rng = cell.Parent.Range(Mid(formulaStr, 2))
On Error GoTo 0
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
GetValidationList = Application.Transpose(rng.Value)
End If
Else
' It's a comma-separated list
GetValidationList = Split(formulaStr, ",")
End If
End Function
- Save and Enable Macros:
- Press
Ctrl + Sto save your workbook with the VBA code. - Close the VBA editor.
- Ensure macros are enabled when you open your workbook. You might need to adjust your macro security settings to enable them.
- Press
- Test the Drop-Down List:
- Go back to your Excel sheet.
- Click on the cell with the drop-down list and select multiple items. Each selection should be added to the cell, separated by a comma.
Important step to remove or edit selected values
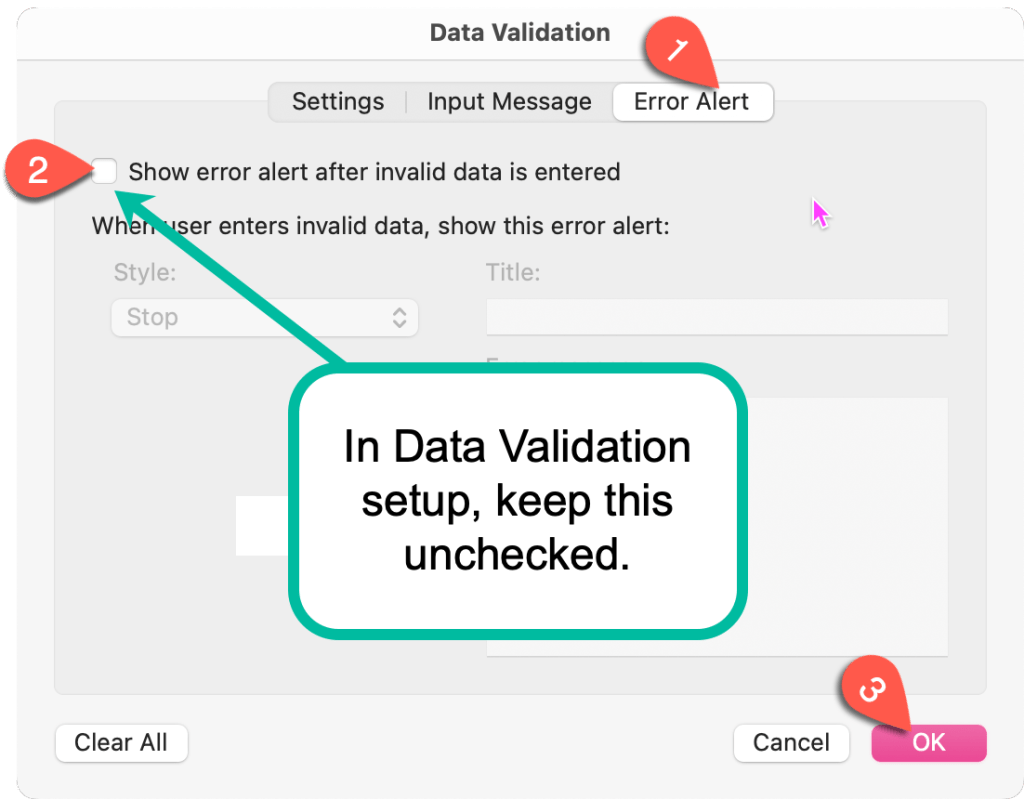
Relax Data Validation: If you want to remove items without errors, set your data validation Error Alert to Warning or Information instead of Stop.
This should set up a drop-down list that allows for multiple selections in Excel using VBA.
Single Drop-Down List on a Specific Sheet in Excel – Code Explanation
< I will update the code explanation soon >
Technique 2: Apply to Any Drop-Down List Throughout the Workbook
This method allows for multiple selections in any drop-down list across the entire workbook.
Steps:
- Create Your List: Enter your list of items in a column and define the range.
- Create the Drop-Down List: Use data validation to create drop-down lists wherever needed.
- Enable Multiple Selections with VBA:
- Open the VBA editor (Alt + F11).
- Insert the following code in the
ThisWorkbookcode window:
'---------------------------------------------------------------
' Purpose : Enable multi-select drop-down across the entire workbook
' while allowing partial edits (removing individual items) and
' the ability to clear the cell completely.
'
' How it works:
' 1) For any single-cell change, check if the cell has list-based data validation.
' 2) If the user selected exactly one new item from the drop-down,
' we append it to existing items, unless it’s already there (to avoid duplicates).
' 3) If the user cleared or manually edited the cell, we allow that change to stand.
'---------------------------------------------------------------
Private Sub Workbook_SheetChange(ByVal Sh As Object, ByVal Target As Range)
On Error GoTo CleanExit
' Ensure only one cell is changed at a time
If Target.Count > 1 Then GoTo CleanExit
' Check if cell has data validation of type List
If Not HasDataValidation(Target) Then GoTo CleanExit
' Temporarily disable events to avoid looping
Application.EnableEvents = False
Dim newValue As String
Dim oldValue As String
' Capture what the user entered/selected
newValue = Target.Value
' Undo the change to get the old value
Application.Undo
oldValue = Target.Value
' Restore the new value to the cell
Target.Value = newValue
' If the user cleared the cell, allow it to remain blank
If newValue = "" Then
' Nothing extra needed; the cell is now blank.
Else
' Fetch the valid items from the data validation source
Dim validationItems As Variant
validationItems = GetValidationList(Target)
Dim userPickedFromList As Boolean
userPickedFromList = False
' Check if newValue exactly matches ONE item in the drop-down
If Not IsEmpty(validationItems) Then
Dim i As Long
For i = LBound(validationItems) To UBound(validationItems)
If Trim(newValue) = Trim(validationItems(i)) Then
userPickedFromList = True
Exit For
End If
Next i
End If
' If user selected a valid drop-down item and the old cell wasn't empty
If userPickedFromList And (oldValue <> "") Then
' Split the old cell contents by commas
Dim oldArray As Variant
oldArray = Split(oldValue, ",")
Dim alreadyExists As Boolean
alreadyExists = False
' Check if newValue already exists in oldValue
For i = LBound(oldArray) To UBound(oldArray)
If Trim(oldArray(i)) = Trim(newValue) Then
alreadyExists = True
Exit For
End If
Next i
If Not alreadyExists Then
' Append new item with a comma
Target.Value = oldValue & ", " & newValue
Else
' Do not duplicate it
Target.Value = oldValue
End If
' If user selected a valid drop-down item and old cell was empty
ElseIf userPickedFromList And (oldValue = "") Then
' Just put the new item in the cell
Target.Value = newValue
Else
' The user typed/edited manually rather than picking a single list item
' -> We respect the manual edit and leave newValue as is.
' (No extra code needed, since Target.Value = newValue already.)
End If
End If
CleanExit:
' Re-enable events
Application.EnableEvents = True
End Sub
'---------------------------------------------------------------
' Checks if the cell has data validation of type List (3).
'---------------------------------------------------------------
Function HasDataValidation(cell As Range) As Boolean
Dim validationType As Long
On Error Resume Next
validationType = cell.Validation.Type
On Error GoTo 0
HasDataValidation = (validationType = 3)
End Function
'---------------------------------------------------------------
' Returns the drop-down list items as a 1D array (if any).
' Handles both direct typed lists (comma-separated) and range references.
'---------------------------------------------------------------
Function GetValidationList(cell As Range) As Variant
Dim formulaStr As String
On Error Resume Next
formulaStr = cell.Validation.Formula1
On Error GoTo 0
If Left(formulaStr, 1) = "=" Then
' It's referencing a range or named range
Dim rng As Range
On Error Resume Next
Set rng = cell.Parent.Range(Mid(formulaStr, 2))
On Error GoTo 0
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
GetValidationList = Application.Transpose(rng.Value)
End If
Else
' It's a comma-separated list
GetValidationList = Split(formulaStr, ",")
End If
End Function
- Save and Enable Macros:
- Press
Ctrl + Sto save your workbook with the VBA code. - Close the VBA editor.
- Ensure macros are enabled when you open your workbook. You might need to adjust your macro security settings to enable them.
- Press
Explanation of VBA Code for Multi-Select Drop-Down List in Any Worksheet
- Event Trigger:
Private Sub Workbook_SheetChange(ByVal Sh As Object, ByVal Target As Range): This subroutine triggers whenever a change is made to any cell in any sheet within the workbook.
- Variable Declaration:
Dim OldValue As String: Declares a variable to store the previous value of the cell before the change.Dim NewValue As String: Declares a variable to store the new value of the cell after the change.
- Error Handling:
On Error GoTo Exitsub: If an error occurs, the code jumps to theExitsublabel to safely exit the subroutine.
- Check for Multiple Cell Changes:
If Target.Count > 1 Then GoTo Exitsub: Ensures the code only runs for single-cell changes.
- Data Validation Check:
If Not HasDataValidation(Target) Then GoTo Exitsub: Calls theHasDataValidationfunction to check if the changed cell has data validation of type list applied to it. If not, the subroutine exits.
- Prevent Recursive Events:
Application.EnableEvents = False: Temporarily disables event triggers to prevent the subroutine from being called recursively.
- Retrieve Old and New Values:
NewValue = Target.Value: Stores the new value entered in the cell.Application.Undo: Reverts the cell to its previous value.OldValue = Target.Value: Stores the old value of the cell.Target.Value = NewValue: Restores the new value to the cell.
- Concatenate Values:
If OldValue <> "" Then: Checks if the old value is not empty.If NewValue <> "" Then: Checks if the new value is not empty.Target.Value = OldValue & ", " & NewValue: Concatenates the old and new values, separated by a comma.
Else: If the new value is empty.Target.Value = OldValue: Restores the old value to the cell.
Else: If the old value is empty, no concatenation is needed.
- Enable Events:
Exitsub: Application.EnableEvents = True: Re-enables event triggers before exiting the subroutine.
- Data Validation Function:
Function HasDataValidation(cell As Range) As Boolean: This function checks if a cell has data validation of type list applied.Dim validationType As Long: Declares a variable to store the validation type.On Error Resume Next: Skips errors that occur when checking the validation type.validationType = cell.Validation.Type: Retrieves the validation type of the cell.On Error GoTo 0: Resets normal error handling.HasDataValidation = (validationType = 3): ReturnsTrueif the validation type is 3 (list).
Conclusion
Using these techniques, you can easily enable multiple selections in Excel drop-down lists, enhancing the functionality of your spreadsheets. Whether you need this feature for a specific list on a single sheet or for any list across your entire workbook, these VBA solutions provide a flexible and powerful way to achieve your goal.